Thoracoscopy
Thoracoscopy
Minimally invasive surgery is considered one of the most important milestones in surgery in recent decades. In this way, operating in the thoracic cavity of children has greatly evolved over the last 20 years, from an open approach to an extremely safe thoracoscopic procedure.
Thoracoscopic procedures were formerly considered “state of the art” in pediatric patients, but are now the standard of treatment for many disease conditions in pediatric surgical centers.
What is Thoracoscopy?
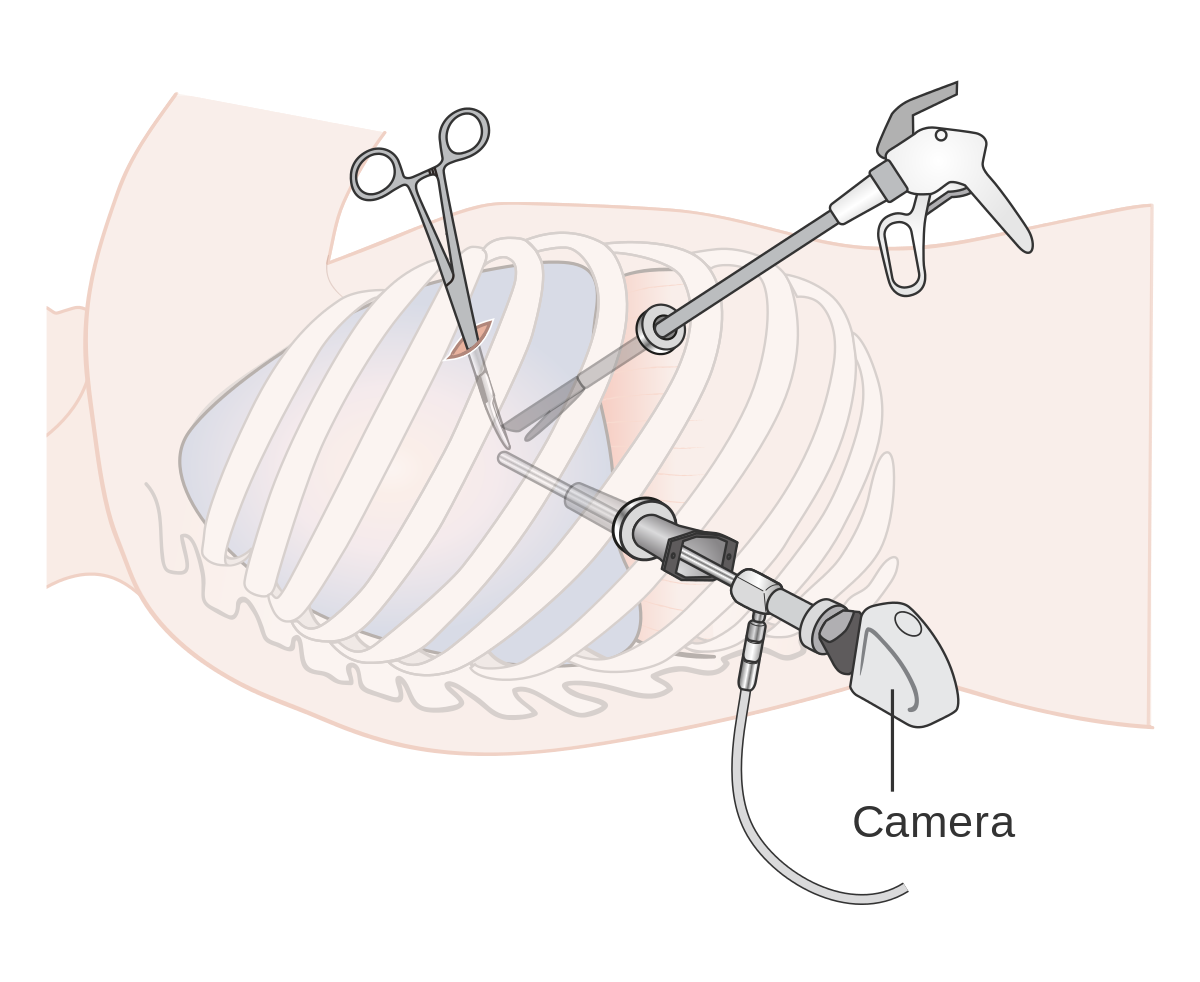
Thoracoscopy is a medical procedure that allows a doctor to examine the area within the chest (outside of the lungs).
This is done with a thoracoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a light, and a small video camera on the end. The tube is inserted via a small incision towards the bottom of the shoulder blade between the ribs.
Thoracoscopy is occasionally used as part of a VATS operation (video-assisted thoracic surgery).
What pediatric condition required a thoracoscopy?
- Diaphragmatic hernia
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus Ligation
- Esophageal Surgery
- To take Lung biopsy
- Lobectomy
- Empyema
- Mediastinal tumor and cyst
What are the different types of thoracoscopy?
There are two types of thoracoscopy procedures that are commonly performed:
Surgical Thoracoscopy: This method needs the patient to be sedated and is appropriate when the thoracoscopic surgery serves both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Medical Thoracoscopy: This method is significantly less invasive than surgical thoracoscopy, requiring just minor incisions to complete the procedure. This method serves mainly to perform a biopsy of the lungs, chest cavity, or pleural cavity.
What is needed before the procedure?
Most patients have imaging studies in advance to fully plan the operation.
Prior to the surgery, the patient may need to avoid eating, drinking, as well certain drugs. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
Special instructions and care that may be required in very young children will be informed to the parents before surgery.
What happens during the procedure?
Each thoracoscopic procedure is customized to the childs specific problem.
To begin, a half-inch incision is made in the chest to allow for the passage of a hollow tube. To observe or check the lungs and chest cavity, a thoracoscope is introduced via the incision.
If necessary, surgical tools may be placed via additional small incisions to execute the surgery under video supervision as seen through the thoracoscope.
Following the procedure, a small drain is usually left in the chest to remove air or fluid.
What are the risks?
Thoracoscopy may result in infection, hemorrhage, pneumonia, and a collapsed lung. These are unusual, however, and most patients experience no additional complications after surgery.
Many children are discharged from the hospital within 48 hours following surgery.
If a chest tube is left in place, it is normally withdrawn the following day at the patient’s bedside.
Children will be encouraged to have breathing exercises to re-expand the lung and help prevent pneumonia.
What are the Advantages of Thoracoscopy?
- It may be done under general anesthesia with a breathing tube or under mild sedation without a breathing tube.
- Thoracoscopy improves the capacity to detect pleural illness and determine the cause of pleural fluid accumulation.
- Thoracoscopy is used for both surgical and diagnostic purposes.
Dr. Adwait Prakash is a senior Pediatric surgeon in Indore, skilled in all thoracoscopy procedures.
To book your appointment Call: 8889588832
