Adrenal Tumors in Children
Adrenal Tumors in Children
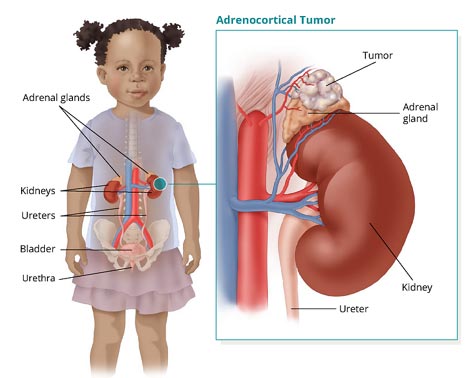
Adrenal tumors are masses that develop in the adrenal gland, the organ that produces hormones in response to physical and mental stress.
Adrenal tumors may be functioning or non-functioning, meaning that some produce hormones, and some do not. Extra hormones produced by functioning tumors may induce early puberty, high blood pressure, sweating, headaches, and abdominal discomfort. Non-functioning tumors do not produce excess hormones.
Adrenal tumors types include:
- Adrenal adenomas
- Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACCs)
- Pheochromocytomas
What age group is more frequent for Adrenal Tumors in Children?
Adrenal adenomas are relatively common, affecting 5-10% of the population, while ACCs are rare.
ACCs are more frequent in children under the age of six.
ACCs are more common in girls.
If your child is diagnosed with ACC, doctors advise genetic counseling since many cases are associated with a hereditary cancer disease known as Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
Childhood Adrenal Tumors: Causes and Symptoms
Adrenocortical carcinomas (ACCs) are often associated with hereditary disorders, most notably Li-Fraumeni syndrome. This condition affects 50-80% of pediatric ACC patients. Other conditions that are linked include:
- Type 1 Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN1)
- Lynch’s syndrome
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
- Hemihypertrophy
Pheochromocytomas have been linked to the following conditions:
- Neurofibromatosis
- von Hippel-Lindau disease
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndromes
- Tuberous sclerosis (TS)
- Sturge-Weber syndrome
- Ataxia-telangiectasia
The symptoms of adrenal tumors may vary from child to child. The symptoms will vary depending on the location and type of tumor.
Abdominal pain, fullness, or the presence of an abdominal lump if the tumor does not produce hormones.
If a tumor generates hormones, it may cause weight gain, high blood pressure, or the early beginning of pubertal changes (voice deepening, pubic hair, body odor, acne, or the development of breast tissue).
A pheochromocytoma causes high blood pressure, quick pulse, headache, nausea, and sweating.
Because many of these symptoms might potentially be indicative of other diseases, it is important that your child be assessed by a medical expert.
What are the Treatment Options for Adrenal Tumors in children
Treatment for your child’s adrenal tumor will be determined by the kind of tumor and if it is malignant. Your child’s pediatrician may advise:
Medication: In the case of some types of adrenal tumors, medication may be used as an additional therapy. Before removing a pheochromocytoma, your child’s physician may give blood pressure medication. Doctors may also recommend medicine to address excessive hormone production in tumors that are still functioning.
Surgery may include removal of the whole tumor and surrounding tissue, and perhaps removal of the adrenal gland.
Radiation therapy: A specialized equipment emits high-energy rays that harm or destroy cancer cells and reduce tumors. Doctors often combine radiation treatment with surgery, either before or after the tumor is removed.
Chemotherapy: Before or after surgery, doctors may use chemotherapy, a medication treatment that aims to eliminate or shrink cancer cells.
For more information & consultation on Adrenal Tumors in Children, Get in touch with Dr. Adwait Prakash a Pediatric Surgeon in Indore. will help you out in understanding your problem and guide you through every stage of your treatment.
To book your appointment Call: 8889588832.
