Hernia and Hydrocele
Hernias and hydroceles are common medical conditions in newborns, infants and children.
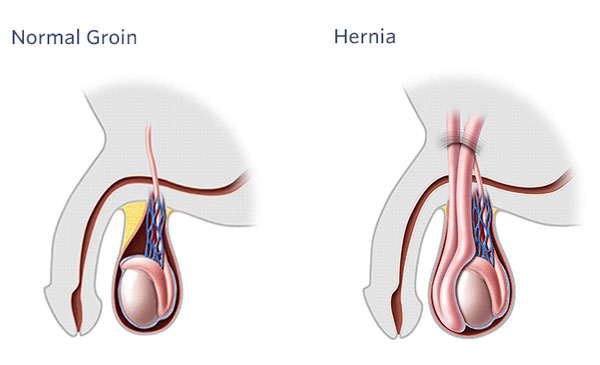
Hernia
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue pushes through a weak point or hole in a muscle wall and into a section of the body where it does not belong. Hernias appear as a protrusion on the body. Hernias seldom resolve on their own and often need surgery.
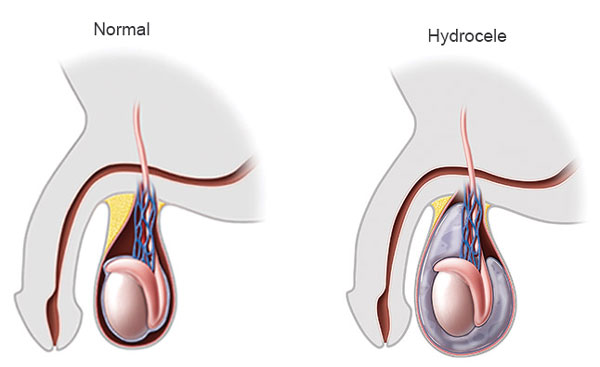
Hydrocele
A hydrocele is a fluid-filled sac that forms around a testicle and causes scrotum enlargement. The testicles form in the abdomen and then migrate down a tube into the scrotum, accompanying a thin-walled sac, throughout development. This sac normally closes itself, and the body absorbs any fluid. Sometimes, the fluid remains. This is referred to as a non-communicating hydrocele. The sac may stay open in certain situations, enabling fluid to flow in and out. This is referred to as a communicative hydrocele. Hydroceles normally disappear during the first two years of life and do not need medical treatment. Hydroceles seldom produce symptoms other than swelling, which may vary in size and frequency.
What are the types of hernia?
The following are the most frequent hernias in children:
- Inguinal hernia– An inguinal hernia arises when a section of the intestines, abdominal contents, ovaries, or fallopian tubes protrude into the groin. This is more common on the right side of the body, although it may happen on either side. This type of hernia affects males more than girls and is more frequent in preterm neonates. Inguinal hernias are common in baby boys with undescended testes and in children with cystic fibrosis. An inguinal hernia may be of varying severity:
- Umbilical hernia-Umbilical hernias develop at the lower abdomen. They are caused by an opening in the abdominal muscles at the lower abdomen or by weak muscles. Membranes or intestines may be able to pass through the opening. Some umbilical hernias heal on their own by the age of three. Umbilical hernias are often reducible and seldom progress to incarcerated or strangulated hernias.
- Reducible hernia– Tissues only bulge out with a reducible hernia when under stress or pressure, such as when a child coughs or cries. They are not a serious threat.
- Incarcerated hernia-An incarcerated hernia occurs when tissue, such as a loop of the small or large intestine, becomes trapped in the groin area. This might obstruct or impede the passage of food through the digestive tract.
- Strangulated Hernia-A strangulated hernia is one that cuts off the blood supply to the trapped tissue (such as the intestines or testicles) and must be treated right once to save the affected area.
What are the symptoms of Hernias and hydroceles?
Hernias and hydroceles may cause symptoms ranging from no discomfort or moderate pain to severe consequences. Among the symptoms are:
- Swelling
- Pain
- Redness
- Fever and Vomiting
Diagnosis of Hernias & Hydroceles
- Clinical examination. The doctor will examine your child and any present bulges or lumps.
- The doctor will ask your child to sit and stand to examine how the bulge moves in various positions if she has a hernia.
- A hydrocele will be examined similarly to a hernia, and swelling in the scrotal sac will be checked.
- Ultrasound. Whether the doctor cannot identify whether the bulge is a hernia or a hydrocele, or if additional tissue is caught in the hernia, a painless ultrasound check will be performed. Ultrasound imaging creates pictures of inside organs and tissues by using sound waves. This helps the surgeon see what is happening and if surgery is required.
What are the Treatment options for Hernia and hydroceles?
Monitoring. Whether an umbilical hernia or a hydrocele is not causing discomfort or threatening other body structures, the doctor will monitor your child’s condition for nine months to two years to determine if the condition heals on its own.
Surgery. If a hernia causes discomfort in the intestines or other tissues are trapped, or if a hydrocele remains beyond the age of two years and continues to grow in size, surgery will be performed. This treatment restores weak muscles and returns tissues and organs to their proper location in the case of a hernia. The procedure for a hydrocele is quite similar, as it also removes the fluid-filled sac.Surgical therapies give outstanding results in situations when the hernia or hydrocele does not cure on its own.
For more information & consultation on Hernia and Hydrocele, Get in touch with Dr. Adwait Prakash a Pediatric Surgeon in Indore. will help you out in understanding your problem and guide you through every stage of your treatment.
To book your appointment Call: 8889588832.
